Mercurial barometer
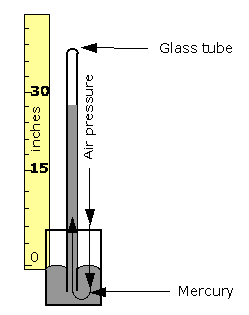
Based on a principle developed by Evangelista Torricelli in 1643, the Mercurial Barometer is an instrument used for measuring the change in atmospheric pressure. It uses a long glass tube, open at one end and closed at the other. Air pressure is measured by observing the height of the column of mercury in the tube. At sea level, air pressure will push on the mercury at the open end and support a column of mercury about 30 inches high. If you used water instead of mercury, you would need a glass tube over 30 feet in length.
As atmospheric pressure increases, the mercury is forced from the reservoir by the increasing air pressure and the column of mercury rises; when the atmospheric pressure decreases, the mercury flows back into the reservoir and the column of mercury is lowered.
Public Domain
Public Domain is a copyright term that is often used when talking about copyright for creative works. Under U.S. copyright law, individual items that are in the public domain are items that are no longer protected by copyright law. This means that you do not need to request permission to re-use, re-publish or even change a copy of the item. Items enter the public domain under U.S. copyright law for a number of reasons: the original copyright may have expired; the item was created by the U.S. Federal Government or other governmental entity that views the things it creates as in the public domain; the work was never protected by copyright for some other reason related to how it was produced (for example, it was a speech that wasn't written down or recorded); or the work doesn't have enough originality to make it eligible for copyright protection.